
A Cost-Benefit Breakdown of Ecommerce Platforms & Custom Development
That’s right. Billions. This staggering figure underscores the inexhaustible expansion and potential of the online shopping sector, prompting many traditional offline businesses to venture into e-commerce channels. In other words, if you can’t beat’em, join ’em!
Easier said than done, however. Many brands’ first forays into e-commerce involve third-party platforms as their main battleground. These platforms are typically user-friendly and are designed to have you up and selling with minimal effort on the back end of things. But while setting up your store on a third-party platform is quick and (usually) painless, factors such as transaction fees, customer service management, and brand autonomy are often outside of your control.
Throughout this blog series, we’ll explore the various options for running an e-commerce business. We’ll explore the costs and benefits of each approach, with a particular focus on the long-term advantages of custom e-commerce development.
What are the Benefits of Setting Up an E-commerce Website? 4 Advantages of E-commerce Website Development
Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, having your own e-commerce website offers a distinct advantage over relying on third-party platforms. Here are four key benefits to consider:
1. Enhancing Consumer Experience
Through an e-commerce site, your consumers can easily browse through your products, including product information and specifications offered by your brand or enterprise. Online stores also normally facilitate multiple payment methods and home delivery services, minimizing shoppers’ inconvenience and leading to more consistent customer satisfaction metrics.
2. Saving on Third-Party Platform Fees
Operating an e-commerce channel through third-party platforms often involves platform fees or listing fees, which can take a generous bite out of your profits. However, higher prices on the platform run the risk of actually reducing the competitiveness of your products.
If you want to focus on long-term e-commerce operations, setting up your own e-commerce website can help you remove concerns about platform fees, save on expenses, and ensure a more sustainable business model.
3. Data Collection and Analysis Utilization
Third-party platforms offer a convenient starting point for e-commerce, but they often leave you in the dark regarding detailed customer insights. Setting up your own e-commerce website leads to a treasure trove of valuable sales data, such as revenue, sales volume, and average order value. Moreover, integrating your custom e-commerce platform with your internal systems, like CRM, logistics, and supply chain information, gives you a holistic view of your business
Moreover, it allows you to establish a visual data management backend, granting instant access to all report data at a glance.
Comparing the Three Ways to Set Up an Online Store! Which E-commerce Platform Setup Method is Best: Open-source, Custom Development, or using Third-Party E-commerce Platforms?
The ideal website platform for your e-commerce store depends on your specific needs and resources. Here’s a breakdown of the most common options available.
1. Open-Source Website Building Platforms
Advantages of Open-Source Website Building Tools:
- Ready-made website templates and designs: Under the platform framework, dozens of ready-made templates are available for businesses to create e-commerce websites that match their brand style and characteristics.
- Backend functionality for customer relationship management: Through the platform backend, businesses can directly gather and manage consumer information, which naturally aids in managing customer relationships and implementing personalized marketing differentiation.
- Installation of auxiliary plugins: Depending on the platform framework and its settings, your business can add various functions where necessary to optimize the sales process and improve the shopping experience. For example, you can install a plugin for live chat support, another plugin for social media integration, and a third for advanced analytics tools.
- Lower initial costs compared to custom e-commerce development: Third-party platform long-term rental fees are generally more affordable than starting from scratch to build a website, making them a reliable choice for businesses, brands, or individual e-commerce entities with medium to low revenue who cannot afford significant upfront capital investment.
Website Building Tools:
- Requires basic website-building know-how: Even though third-party platforms offer accessible website-building functions and tutorials, making complex settings adjustments still requires basic knowledge of website building.
- Limited template options: Existing platform design templates are designed for fast setup, but they are often limited in terms of scope. If you want to craft a wholly original e-commerce website design, then you’ll need to incur additional website development and design costs.
- Functionality restricted by platform framework: The current e-commerce functions of most third-party platforms are aimed at the Business-to-Consumer (B2C) industry. If your business or brand operates in a mixed B2B or B2B2C industry, the functionality of third-party website-building tools might prove insufficient in handling complex shopping processes, such as inter-enterprise quoting and ordering, or managing multiple customer accounts with different pricing structures.
2. Third Party E-commerce Platforms
Unlike using an open-source platform to self-develop a shopping site, third-party e-commerce hosting platforms focus on “e-commerce” only and do not provide other website setups. These hosting platforms are specifically designed for e-commerce, with common examples including Shopify, WooCommerce, and Magento.
Advantages of third-party E-commerce platforms:
- Immediate store setup: E-commerce platforms allow for rapid setup, with stores being ready to rock in as little as 10 minutes.
- Low initial investment and entry barriers: These platforms provide free or low-cost setup plans, allowing businesses or brands to enter the e-commerce domain without significant initial financial investment.
- Comprehensive payment and logistics features: Since these platforms specialize in e-commerce, they boast complete sales, payment, and inventory management functions. Compared to using third-party platforms to build an e-commerce site, there’s no need to spend additional time integrating additional e-commerce-related tools.
Disadvantages of third-party E-commerce platforms:
- Potential for price hikes: E-commerce platform providers can adjust their pricing structure anytime, leaving you with no choice but to accept the changes or stop using the platform.
- Challenges in data collection: Backend operations may be subject to the policies of the e-commerce platform, making it tricky for businesses to fully access all sales-related data or even obtain complete customer information, which is crucial for customer relationship management and marketing.
- Difficulty transferring data to other platforms: As businesses expand and platform fees adjust, there may be a desire to migrate to other platforms or self-host entirely. However, transferring all customer data and sales records off these sites is rarely straightforward. Thus, it’s wise to consider your long-term goals when deciding how to set up the website initially.
- Limited website design freedom: Unlike self-hosted websites, e-commerce platforms restrict flexibility in changing content, making it challenging to design a front-end page that meets the specific needs of your business or brand.
- Information security concerns: E-commerce platforms’ security measures are generally solid, but their popularity also makes them popular targets for malicious attacks, data breaches, or credit card fraud.
3. Self-Hosting E-commerce Websites: Custom E-commerceWebsite Development
Whether it’s self-hosted websites or third-party e-commerce platforms, both feature relatively mature systems. However, business complexity is often based on factors such as the number of products, the complexity of the sales process, the need for integration with other systems, information security, and industry specificity. As such, many large enterprises still opt for custom e-commerce development services.
Advantages of Custom E-commerce Website Development:
- Tailored E-commerce design and content: It is possible to create a complete website framework, both front-end and back-end, tailored to your enterprise, with freedom in customizing e-commerce website design. Any future business expansions or adjustments can be easily accommodated by adding or removing website functions where necessary.
- High security and stability: Custom e-commerce website development offers greater security and stability compared to third-party platforms. Most importantly, your website’s information security is not affected by third-party platform attacks, which saw 206,000 cyber attacks monthly in 2019 alone.
- Cross-platform system integration: Even complex B2B industry processes such as inter-enterprise quoting and ordering can be addressed through custom E-commerce development. It can also integrate and streamline existing systems within your enterprise, allowing data and information to flow between systems. Using a third-party platform setup and integrating internal enterprise information might raise information security concerns, which are generally not a concern with self-developed custom websites.
Disadvantages of Custom E-commerce Website Development:
- Higher costs: There’s no getting around it – the development cost of a single website is higher, whether it’s self-developed or built with professional assistance. A customized site requires greater investment costs and time.
- Requires maintenance and update costs: After a website’s construction, continuous management updates and maintenance are needed to keep it functional, so it’s necessary to hire experienced E-commerce managers or outsource hosting to ensure that the platform remains up to date in terms of privacy and security standards.
Cloud Interactive provides customized e-commerce website development services tailored to the needs of both B2B and B2C industries. If you need website development, just click the link below to fill out our form, and we will arrange for one of our team members to contact you as soon as possible.
4. Listing on Third-Party Marketplaces
With the rise of online shopping, numerous online marketplaces have emerged, each offering comprehensive sales platforms and payment services. These functions allow businesses to list and sell their products on specific digital channels, where consumers can purchase items from various brands in a single location, similar to an online department store. Common third-party marketplaces include Amazon and Etsy.
Advantages of Listing on Third-Party Marketplaces:
- Increased exposure: Listing on popular third-party platforms can help a business leverage its existing user base and traffic, enhancing brand visibility.
Disadvantages of Listing on Third-Party Marketplaces:
- Fees and charges: These platforms charge fees for listing products and making sales, reducing the profit margins in the long run.
- Intense competition: Third-party platforms are filled with vendors in tight competition, making it easy for consumers to compare prices and choose one vendor over another if price is the main differentiator.
- Limited brand recognition: Since purchases are conducted through third-party platforms, consumers are prone to remembering the marketplace itself rather than the brand, making it difficult to build consumer loyalty. How many times have you bought an item off Amazon and received follow-up emails from them compared to Amazon itself?
How to Set Up an E-commerce Website?
Are you planning to build a fully functional e-commerce website? Below are the six steps you will encounter when setting one up. These steps may vary slightly depending on the setup method and platform chosen.
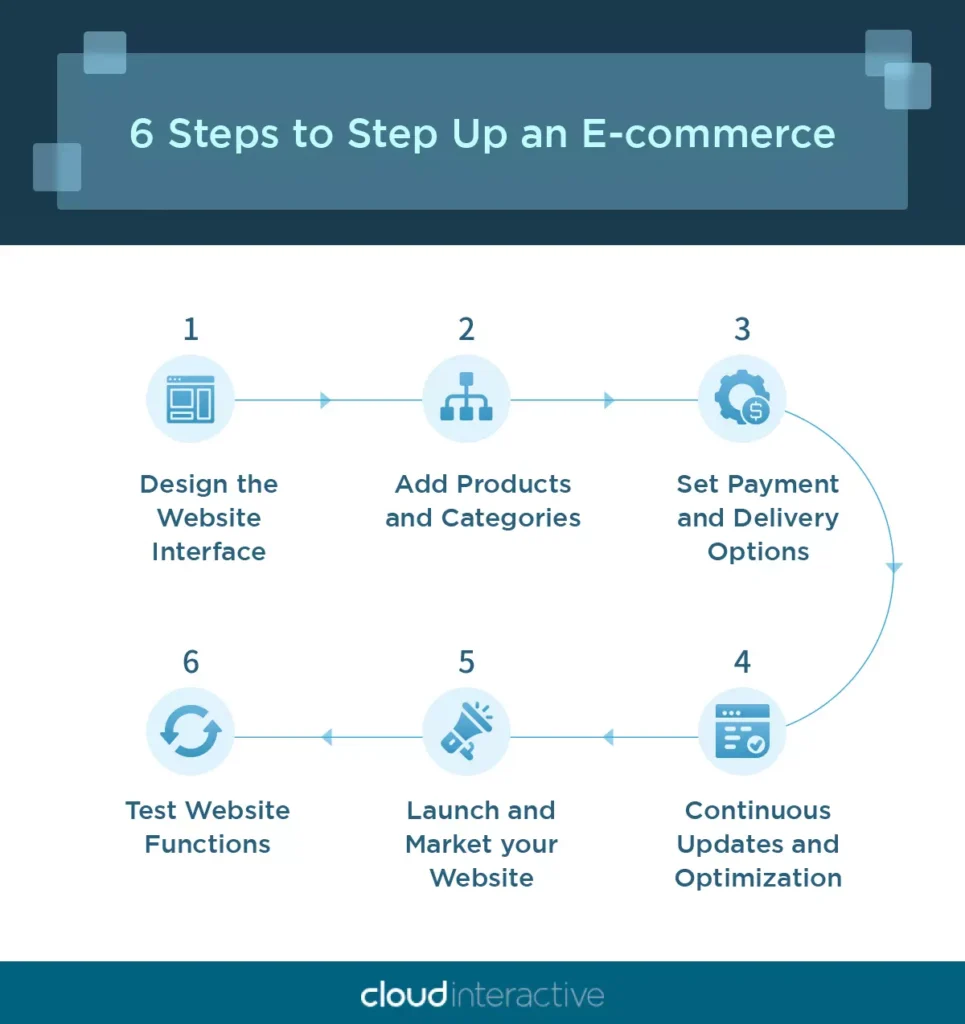
1. Design the Website Interface
Whether you are self-hosting or using a third-party e-commerce platform, the most critical first step involves the “website layout”! To leave a good impression on your consumers, your website’s design must be sleek, easy to navigate, and visually distinctive, all while aligning with your brand image.
Compared to third-party or e-commerce platforms, which typically have limitations, custom E-commerce development offers high flexibility in webpage design, allowing customization from the page layout to the font style to meet your business’s needs.
2. Add Products and Categories
Once your basic layout is constructed, you can start adding products to the website, including product pages, names, descriptions, prices, images, and other detailed information. For example, a clothing brand’s products can be categorized into sections such as tops, bottoms, and outerwear.
3. Set Payment and Delivery Options
4. Test Website Functions
Before officially launching your website, you’ll want to conduct an internal test of all functionalities, including adding items to the cart, placing orders, checking out, and updating logistics information. This test ensures that all features work as intended, providing a secure shopping experience for your consumers and avoiding potential disputes that could sully your brand’s reputation.
5. Launch and Market your Website
Once your website’s functionality and stability are confirmed, you’re now ready to promote it through relevant marketing channels, such as digital advertising, social media management, and Search Engine Optimization (SEO). If you have a physical store, your offline promotion efforts can be enhanced by displaying promotional materials for the online store in-house and training your staff to inform customers about it.
6. Continuous Updates and Optimization
After your website goes live, it’s essential to maintain and update its functions and security features year-round. Staying vigilant ensures that your website remains up-to-date and secure, providing a stable shopping experience for your consumers at all times.
Five Essential Features of an E-commerce Website

Product and Content Management
This is a no-brainer – the most important aspect of your online store is the actual products you sell to your consumers! A good product management feature allows you to track current inventory and sales status, easily plan product categories and prices, and set independent payment and shipping options for each product. What’s more, your homepage or sidebar might include carousel content to convey messages to your consumers, which can also be updated through the backend. This functionality makes it easy for your consumers to receive clear and detailed product information while they browse your wares.Shopping Management
Shopping management features allow consumers to add products to their favorite lists, leave reviews on purchased items, and enable you to manage each order’s status, revenue, and invoice issuance through the backend. The system also allows for collecting consumer purchase records and favorite item data for segmented marketing.Promotion Management
Promotion management features help businesses create, edit, and delete various marketing activities on the website, such as site-wide discounts, special item offers, coupon issuance, discount codes, and member tier rewards, all of which can be managed through the promotion management function.Customer Management
Customer management features include allowing consumers to set up personal accounts with their own homepage. During the account creation process, you can collect customer lists for segmented marketing, such as reminding consumers about unpurchased items in their cart or having intelligent customer service inquire if they need assistance when they stay on a page for too long. These features enable businesses to provide personalized services, enhancing customer goodwill towards your brand.Data Analysis and Reporting
A consolidated report of various data in the e-commerce backend is invaluable for any business: sales volume, sales revenue, average order value, and more can be integrated with Google Analytics 4 to continuously analyze user behavior on your website, such as bounce rates and the ratio of items added to the cart but not purchased. These data points are invaluable for helping you optimize your future strategies. Besides the five standard features mentioned above, we can assist Business-to-Business (B2B) industries in setting purchase permissions for different distributors, offering each one different prices and discounts, eliminating the need for manual price negotiations, and integrating the business’s internal ERP system to effectively manage the actual purchase and sales quantities of each product.
How Much Does It Cost to Set Up an E-commerce Website? Does Self-Hosting a Website Cost Money?
1. Self-Hosted Website Costs
If a business or brand wants to set up a fully functional e-commerce website, the following costs should be considered:
Domain Fees
Every website has a domain, which is the address in the online world that helps search engines find your site. Domain fees are usually calculated on an annual rental basis, depending on the level and popularity of the domain. The yearly rental fee typically ranges from $3.49 to $15 per year.
Hosting/Server Fees
After securing a domain, the next step is to establish a “host” or “server” to store website data. The website’s source code is stored on this host for users to access.
Hosts can be either physical or virtual.
A physical host involves setting up an actual computer server within your company, requiring both hardware costs and professional maintenance staff. A virtual host consists in renting a server from a specialized hosting provider, using cloud storage to send data to the provider’s machines, with monthly rental fees that range from $1-15/month.
SSL Certificate Fees
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates ensure user information security on your site by encrypting data transmission and verifying the server’s identity. SSL certificates have become an established practice for all reputable websites today.
SSL certificate fees are calculated annually, and free and paid options are available. The cost varies greatly depending on the certificate’s level, ranging from $8 to $1034 annually.
Website Traffic Fees
Website traffic fees are incurred whenever users visit your site, and you, as the host, must transmit data to their browsers. Hosting plans typically include a certain amount of free traffic, but exceeding this limit incurs additional fees. Pricing varies by hosting provider, with popular hosts such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) costing $0.085/GB up to the first 10TB per month.
Payment and Shipping Setup Fees, Transaction Fees, Service Fees
Depending on the payment and shipping options you provide to your consumers, different setup fees, transaction fees, and service fees apply.
Setup fees are typically charged when your website is initially set up, transaction fees are deducted from each sale, and service fees are periodically charged by some payment or shipping service providers based on contract terms.
Website Template Fees
The template determines your website’s first impression to prospective customers, so make it last! Whether you hire a designer to create a custom template or purchase a ready-made one, there will be associated costs toward making your website stand out.
Web Function Development and Design Quotes
Your website must be functional and user-friendly, including features such as responsive design (RWD), user experience design (UX), and custom backend development. These highly intuitive features are often the highest expenses in self-hosted websites, and the number and complexity of features vary according to the website’s complexity.
Website Maintenance Fees
After setting up your website, ongoing maintenance is necessary to ensure the front, host, server, and database function properly. Maintenance can be handled by in-house professionals or outsourced to specialized companies. Outsourced maintenance costs roughly $20 to $5000 per month.
Taking all these factors into account, you’re looking at putting $300 to $60,000 into website maintenance for building a website through a third-party platform. Many businesses opt for more straightforward “single-page websites” due to lower costs and fewer product listings, costing $2-300/month for outsourced tech support.
Due to its higher complexity and required technical expertise, a fully customized self-hosted e-commerce website can cost from $10,000 to $100,000, depending on how much customization is necessary.
Despite the higher costs associated with originality, many businesses prefer fully tailored solutions because of their stability, flexibility, security, and ability to integrate with internal management systems or apps.
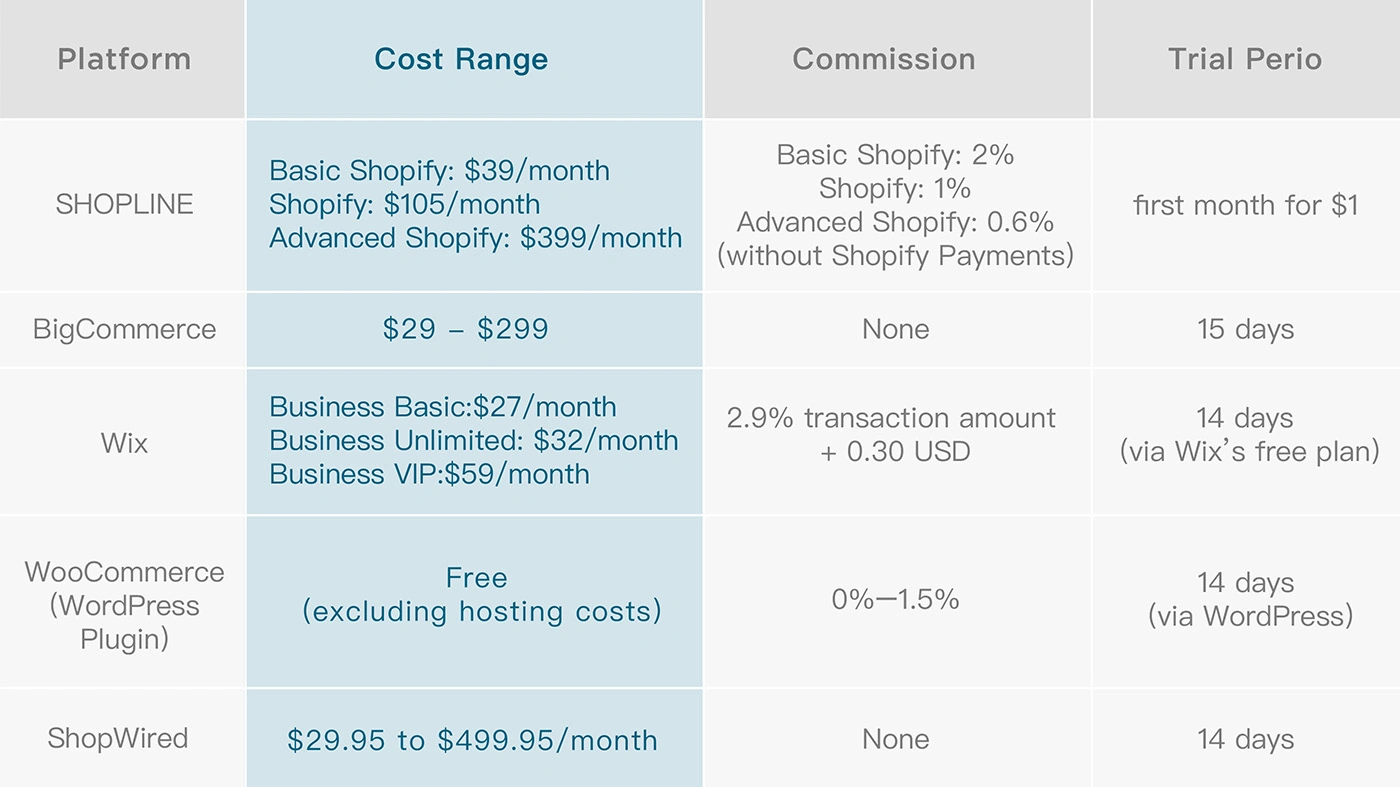
2. Managed E-commerce Website Costs
The cost of a managed e-commerce website depends on the platform’s monthly or annual fees, along with product commission fees.
Some platforms offer free website setup plans, allowing new sellers to create dedicated websites at no initial cost, although these come with significant limitations on customization.
Below is a comparison of the five most popular e-commerce website platforms and their associated costs:
3. The Cost of Listing on the Marketplace
When it comes to transaction and service fees in the listing marketplace, each of the top players has distinct fee structures.
Ultimately, your decision to sell on one marketplace over another will be based on factors such as audience reach, ease of use, branding opportunities, or specific niches. For example, Etsy is particularly attractive if you sell handmade or vintage items, while Amazon appeals to those seeking a broader customer base and stable fulfillment services.
If you’re a business aiming to build a long-term e-commerce presence and foster brand loyalty, it’s definitely worthwhile the initial expense of setting up your own e-commerce website. This approach not only saves on various transaction fees in the long term but also allows you to grow your platform and make incremental improvements based on market demands. This benefit lets you offer more competitive products and services, collect user data, offer customized customer support services, and garner customer loyalty towards your brand in the manner you see fit.
E-commerce Development Service Provider: Cloud Interactive
Cloud Interactive offers custom e-commerce software development services across the B2B and B2C industries. We provide fully comprehensive functionality for product listings, advertising, payment processing, and marketing. For B2B industries, a single platform can connect suppliers with all distributors, managing supply status, inventory updates, pricing, and promotional settings across different channels. This integration enhances your site’s efficiency in both product and channel management. For B2C industries, Cloud Interactive can create a shopping platform tailored to your brand’s image, using responsive web design (RWD) to ensure a clear and cohesive layout across all devices. Additionally, integrating Google Analytics 4 enables your marketing team to analyze data and optimize marketing strategies on the go. Cloud Interactive also develops mobile shopping apps that neatly complement your e-commerce website development solutions. This tandem development ensures that your website and app versions are designed in parallel and integrated with a unified backend. In this way, you can manage products, orders, and promotions on the website and the app from a single backend interface.Further Reading: Cloud Interactive’s Website Development Cases
International Gaming Group
We created a digital game distribution and purchasing platform that offered players a seamless online and offline gaming experience.Design R&D Lab
Our team created integrated internal resources and tools to develop an online collaboration platform.By Cloud Interactive
Meet the masterminds behind the curtain at Cloud Interactive. We're not just software developers - we're also a content crew fuelled by caffeine and a thirst for knowledge. We translate tech jargon into plain English, dissect industry trends, and craft helpful tips that are informative and engaging. So, buckle up and join us on a journey through the ever-evolving and exciting world of technology!


